Welcome to SeqAL
SeqAL is a sequence labeling active learning framework based on Flair.
Please follow the tutorial to know the usage of SeqAL.
Active Learning Cycle
To understand what SeqAL can do, we first introduce the pool-based active learning cycle.
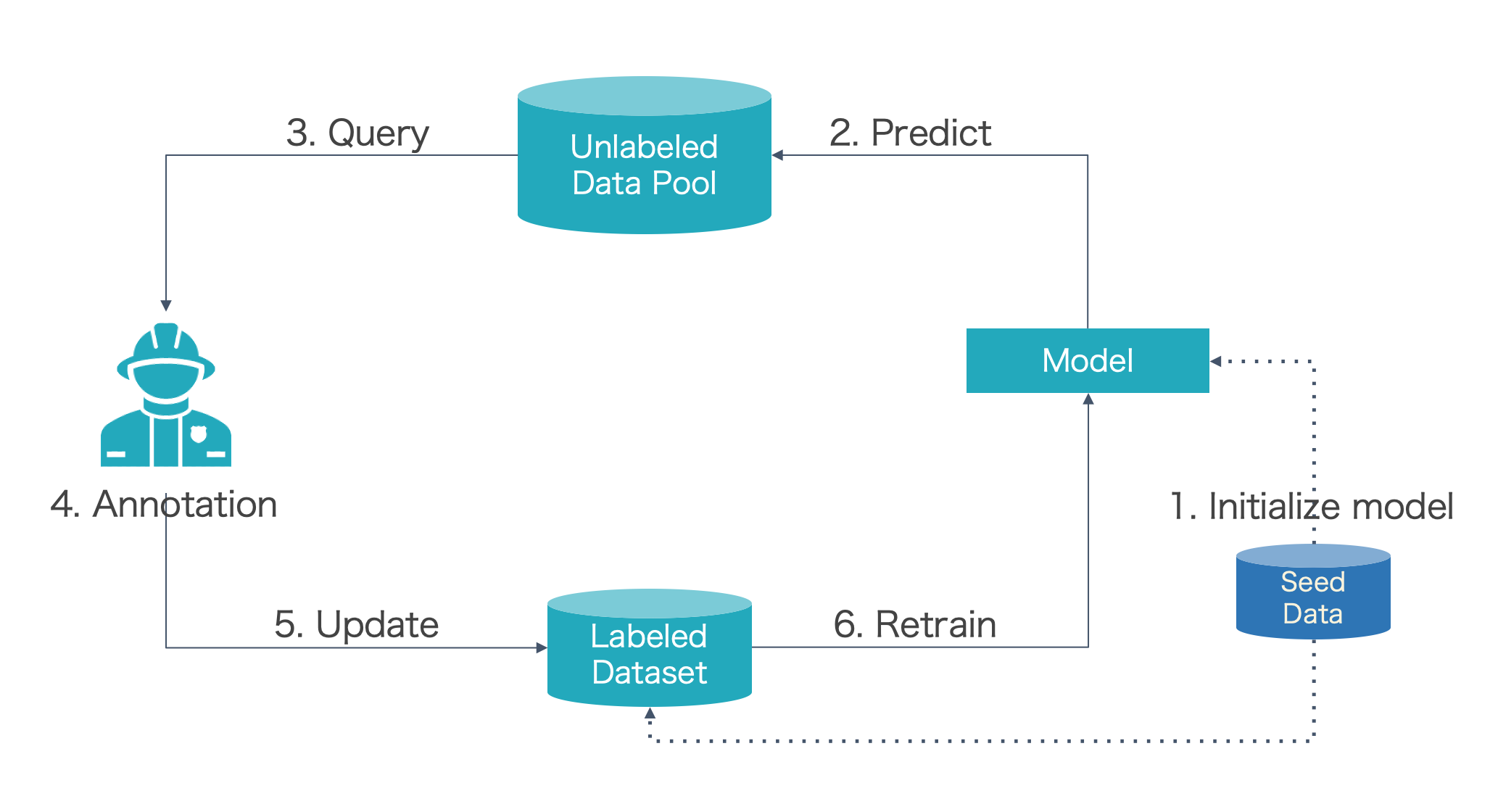
- Step 0: Prepare seed data (a small number of labeled data used for training)
- Step 1: Train the model with seed data
- Step 2: Predict unlabeled data with the trained model
- Step 3: Query informative samples based on predictions
- Step 4: Annotator (Oracle) annotate the selected samples
- Step 5: Input the new labeled samples to labeled dataset
- Step 6: Retrain model
- Repeat step2~step6 until the f1 score of the model beyond the threshold or annotation budget is no left
Simulation of Active Learning Cycle
Run below script can run the active learning cycle. Because there is no 3rd part annotation tool, we just simulate the active learning cycle.
from flair.embeddings import WordEmbeddings
from seqal.active_learner import ActiveLearner
from seqal.datasets import ColumnCorpus, ColumnDataset
from seqal.samplers import LeastConfidenceSampler
# 1. get the corpus
columns = {0: "text", 1: "ner"}
data_folder = "./data/sample_bio"
corpus = ColumnCorpus(
data_folder,
columns,
train_file="train_seed.txt",
dev_file="dev.txt",
test_file="test.txt",
)
# 2. tagger params
tagger_params = {}
tagger_params["tag_type"] = "ner"
tagger_params["hidden_size"] = 256
embeddings = WordEmbeddings("glove")
tagger_params["embeddings"] = embeddings
tagger_params["use_rnn"] = False
# 3. trainer params
trainer_params = {}
trainer_params["max_epochs"] = 1
trainer_params["mini_batch_size"] = 32
trainer_params["learning_rate"] = 0.1
trainer_params["patience"] = 5
# 4. setup active learner
sampler = LeastConfidenceSampler()
learner = ActiveLearner(corpus, sampler, tagger_params, trainer_params)
# 5. initialize active learner
learner.initialize(dir_path="output/init_train")
# 6. prepare data pool
pool_file = data_folder + "/labeled_data_pool.txt"
data_pool = ColumnDataset(pool_file, columns)
unlabeled_sentences = data_pool.sentences
# 7. query setup
query_number = 2
token_based = False
iterations = 5
# 8. iteration
for i in range(iterations):
# 9. query unlabeled sentences
queried_samples, unlabeled_sentences = learner.query(
unlabeled_sentences, query_number, token_based=token_based, research_mode=True
)
# 10. retrain model, the queried_samples will be added to corpus.train
learner.teach(queried_samples, dir_path=f"output/retrain_{i}")
When calling learner.query(), we set research_mode=True. This means that we simulate the active learning cycle. We prepare above code in the examples directory. If you clone SeqAL to your local machine, you should move to the root directory and run below command in terminal.
We also provide a notebook to demonstrate the simulation: active_learning_cycle_research_mode
More detail about research (simulation) mode can be found in Research and Annotation Mode.
Real Case of Active Learning Cycle Implementation
In the real situation, SeqAL should connect to an annotation tool. Below code is a demonstration to show how SeqAL connect with other annotations tools.
from flair.embeddings import WordEmbeddings
from seqal.active_learner import ActiveLearner
from seqal.datasets import ColumnCorpus
from seqal.samplers import LeastConfidenceSampler
from seqal.utils import load_plain_text
from seqal.aligner import Aligner
from xxxx import annotate_by_human # User need to prepare this method to interact with annotation tool
# 0: prepare seed data, validation data, test data, and unlabeled data pool
# - labeled data:
# - seed data: `train_seed.txt`
# - validation data: `dev.txt`
# - test data: `test.txt`
# - unlabeled data:
# - unlabeled data pool: `unlabeled_data_pool.txt`
# 1. get the corpus
columns = {0: "text", 1: "ner"}
data_folder = "./data/sample_bio"
corpus = ColumnCorpus(
data_folder,
columns,
train_file="train_seed.txt",
dev_file="dev.txt",
test_file="test.txt",
)
# 2. tagger params
tagger_params = {}
tagger_params["tag_type"] = "ner" # what tag do we want to predict?
tagger_params["hidden_size"] = 256
embeddings = WordEmbeddings("glove")
tagger_params["embeddings"] = embeddings
# 3. Trainer params
trainer_params = {}
trainer_params["max_epochs"] = 1
trainer_params["mini_batch_size"] = 32
trainer_params["learning_rate"] = 0.1
trainer_params["train_with_dev"] = True
# 4. initialize learner
sampler = LeastConfidenceSampler()
learner = ActiveLearner(corpus, sampler, tagger_params, trainer_params)
# 5. initial training
learner.initialize(dir_path="output/init_train")
# 6. prepare unlabeled data pool
file_path = "./data/sample_bio/unlabeled_data_pool.txt"
unlabeled_sentences = load_plain_text(file_path)
# 7. query setup
query_number = 2
token_based = False
iterations = 5
# initialize the tool to read annotated data
aligner = Aligner()
# 8. iteration
for i in range(iterations):
# 9. query unlabeled sentences
queried_samples, unlabeled_sentences = learner.query(
unlabeled_sentences, query_number, token_based=token_based, research_mode=False
)
# 10. convert sentence to plain text
queried_texts = [{"text": sent.to_plain_string()} for sent in queried_samples]
# queried_texts:
# [
# {
# "text": "I love Berlin"
# },
# {
# "text": "Tokyo is a city"
# }
# ]
# 11. send queried_texts to annotation tool
# annotator annotate the queried samples
# 'annotate_by_human' method should be provide by user
annotated_data = annotate_by_human(queried_texts)
# annotated_data:
# [
# {
# "text": ['I', 'love', 'Berlin'],
# "labels": ['O', 'O', 'B-LOC']
# }
# {
# "text": ['Tokyo', 'is', 'a', 'city'],
# "labels": ['B-LOC', 'O', 'O', 'O']
# }
# ]
# 12. convert data to sentence
queried_samples = aligner.align_spaced_language(annotated_data)
# 13. retrain model, the queried_samples will be added to corpus.train
learner.teach(queried_samples, dir_path=f"output/retrain_{i}")
First, we should provide the 4 files to SeqAL. The 3 labeled datasets (seed data, valid data, test data) and 1 unlabeled dataset (data pool). If you want to use the existing dataset included in Flair, you can follow the data_preparation notebook. Then you only need to provide the unlabeled dataset.
If the annotation tool if the only interface that the user can interactive, the annotation tool should transfer the 4 files to SeqAL.
We provide the script in examples/active_learning_cycle_annotation_mode.py and the notebook to explain in detail: active_learning_cycle_annotation_mode